Main Fields Of Application
Learn where to effectively integrate Angiodroid The CO2 Injector into your clinical practice, why it is beneficial for patient care
Therapeutic Indications To The Use Of CO2 In Angiography
CO2 angiography is a medical imaging method that employs carbon dioxide as a contrast medium to visualize blood vessels. It serves mainly as an alternative to traditional iodinated contrast angiography, particularly in cases where iodinated contrast is not advisable.
The Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR, measured in mL/min/1.73m2) is a key indicator of kidney function and is the most crucial clinical parameter when assessing the use of CO2 as a contrast medium in angiography. Other risk factors, such as albuminuria, which affects therapeutic indications, must also be considered.
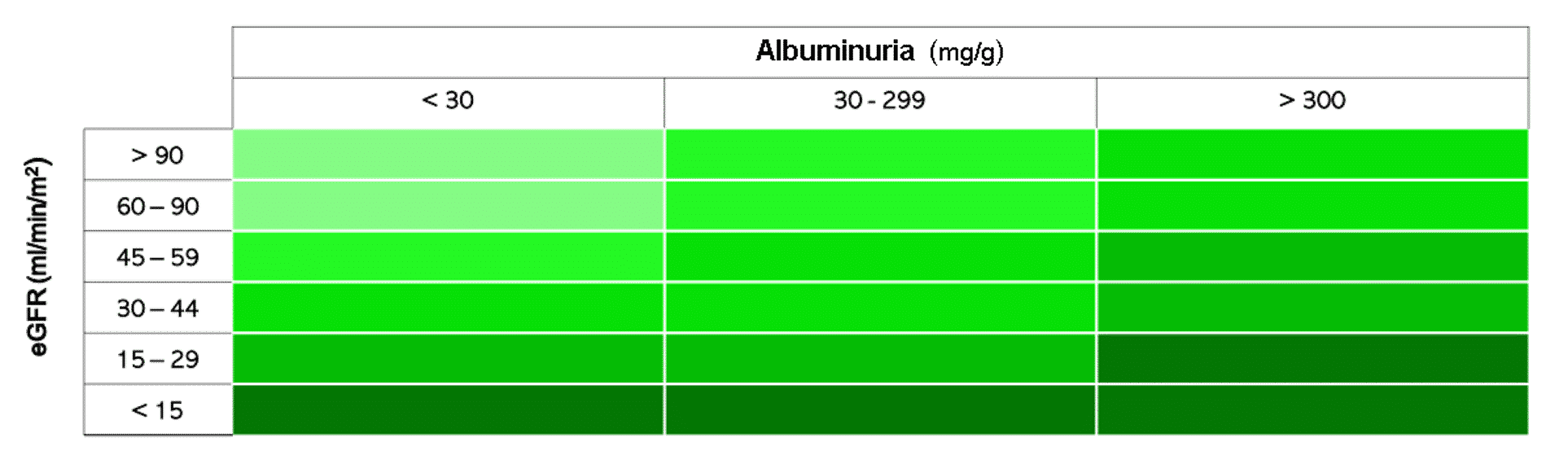
Angiodroid Advantages
Why the use of Angiodroid The CO2 Injector is recommended in particular procedures
The use of CO2 as a Contrast Agent has been demonstrated to provide considerable advantages in many types of intervention and in different fields, i.e. Vascular Surgery, Interventional Radiology and Interventional Angiology.
AVF creation and maintenance

Patients with a fistula who are undergoing hemodialysis and have severe renal insufficiency can benefit from using CO2 as a contrast agent. Since CO2 is not nephrotoxic, it is ideal for use during the creation and maintenance of fistulas, as well as in procedures related to fistula malformations.
IVC Filter

Automated CO2 injection is capable of mapping venous anatomy to guarantee accurate filter positioning. CO2 venography verifies filter placement and inspects for issues such as perforation or thrombosis. By employing automated CO2 systems, clinicians can visualize vascular structures safely and effectively, improving the success rate and safety profile of Inferior Vena Cava filter procedures.
Abdominal Aorta
 Aortogram is usually the step before the intervention.
Aortogram is usually the step before the intervention.
Performing the exam by using CO2 can drastically reduce the amount of iodine to be injected to the patient (Diagnostic and Interventional).
Endoleaks detection

Due to the low viscosity of carbon dioxide (CO2), the process of detecting type II endoleaks becomes significantly easier, safer, and more efficient compared to traditional methods. This low viscosity allows CO2 to flow smoothly and penetrate areas that might be difficult to reach with other contrast media, enhancing the visibility and accuracy of the detection process. As a result, medical professionals can identify and address these endoleaks with greater precision and confidence, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
EVAR

Using CO2 in EndoVascular Aneurysm Repair procedures reduces iodine amount, lowering Contrast Induced-Acute Kidney Injury risk and hemodialysis need. Automated CO2 injection improves image quality and reduces complications in EVAR procedures, aiding accurate stent graft placement. Angiodroid's system enhances procedural outcomes and CO2 helps detect endoleaks, reducing hospitalization in Fenestrated EVAR.
Gastrointestinal bleeding

CO2 is highly buoyant, and ventral arteries are more effectively enhanced when in the supine position. It is significantly less viscous than iodinated contrast medium, allowing it to easily fill collateral and stenotic blood vessels. Consequently, bleeding from small and spastic blood vessels can be visualized. CO2 has a high diffusive capacity and expands considerably when it leaks from a blood vessel into the intestinal tract, which may facilitate the identification of bleeding. Additionally, the vasodilatory effects of CO2 can increase blood flow and lead to further extravasation, serving as a provocative agent but with a lower risk of bleeding complications compared to others.
Embolization

The low viscosity of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is approximately 400 times lower than that of iodinated contrast medium (ICM), allows for the rapid and efficient opacification of the small blood vessels that supply the tumor masses. This is a significant advantage because these small vessels are often challenging to visualize and opacify using traditional iodinated contrast media. The unique properties of CO2 enable it to flow more easily and penetrate these tiny vascular structures, providing clearer imaging results and enhancing the ability to assess and treat tumor-related conditions.
Renal denervation
 CO2 is used in renal denervation procedures as an alternative or supplement to iodinated contrast agents primarily to enhance safety and procedural outcomes. Renal denervation (RDN) aims to deactivate sympathetic nerve endings along the renal arteries to reduce hypertension, a condition closely tied to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Using iodinated contrast in RDN poses a significant risk of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), especially in patients with reduced kidney function (eGFR < 45 mL/min/1.73 m²).
CO2 is used in renal denervation procedures as an alternative or supplement to iodinated contrast agents primarily to enhance safety and procedural outcomes. Renal denervation (RDN) aims to deactivate sympathetic nerve endings along the renal arteries to reduce hypertension, a condition closely tied to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Using iodinated contrast in RDN poses a significant risk of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), especially in patients with reduced kidney function (eGFR < 45 mL/min/1.73 m²).
CO2 angiography allows for significantly lower use of iodinated contrast, reducing its volume from hundreds of milliliters (e.g., 200–250 mL in some studies) to as little as 9–10 mL when combined with CO2. This approach minimizes renal exposure to toxic agents, helping preserve kidney function and supporting better procedural outcomes. Additionally, CO2’s safety profile makes it a valuable choice for imaging in patients with CKD, ensuring that the primary objective of RDN—sustained reduction of hypertension—is not compromised by contrast-induced complications.
TIPS
 Currently, CO2 is the sole contrast agent capable of opacifying the portal vein through an injection from the hepatic vein. Its low viscosity also facilitates the assessment of critical conditions related to stenosis or occlusion of the portal vein.
Currently, CO2 is the sole contrast agent capable of opacifying the portal vein through an injection from the hepatic vein. Its low viscosity also facilitates the assessment of critical conditions related to stenosis or occlusion of the portal vein.
There is no risk of hepatotoxicity.
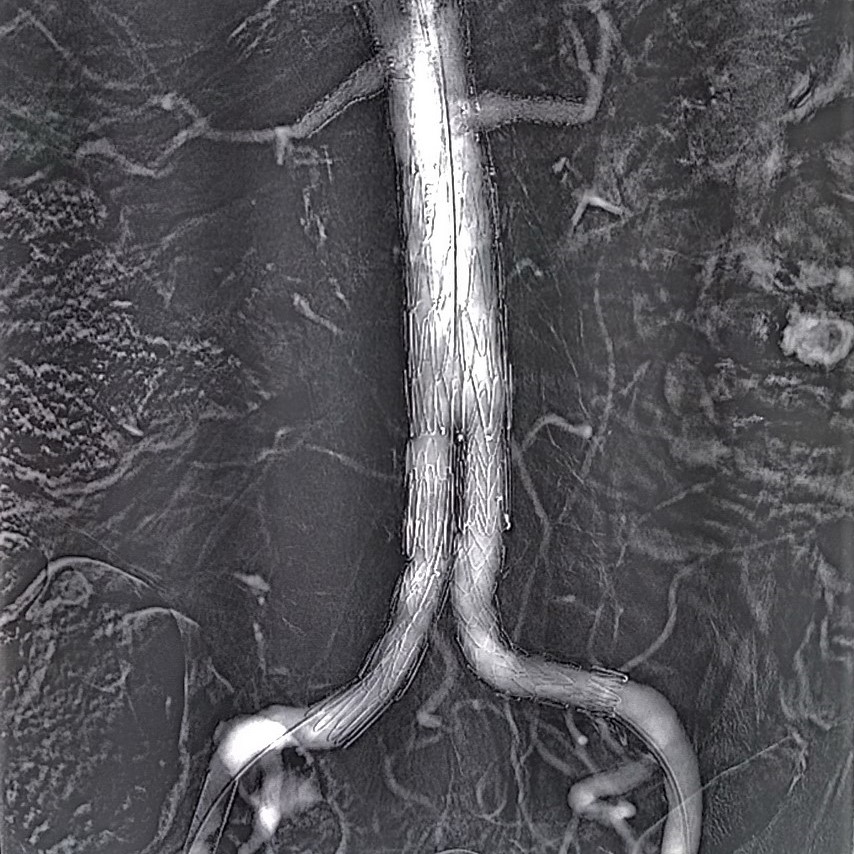
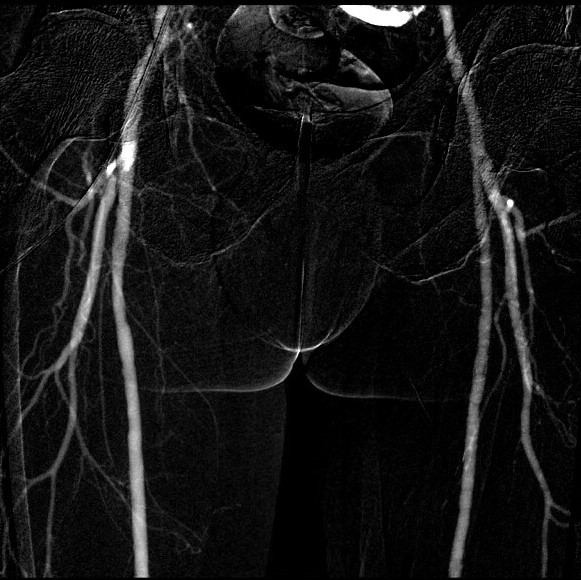
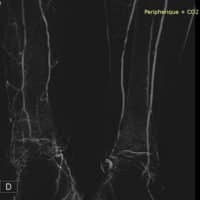
Lower Limbs

CO2 is highly effective for visualizing distal vessels and small collateral arteries in peripheral arterial disease due to its buoyancy and low viscosity. Automatic injection systems enhance safety and efficacy by delivering precise CO2 volumes at controlled pressures, improving image quality and reducing complications. This method is particularly beneficial for patients with Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI), as it provides detailed imaging crucial for planning revascularization procedures without nephrotoxic effects, supporting safer and more effective interventions.
PTA

Conducting the examination with CO2 can significantly decrease the quantity of iodine required for injection into the patient. Due to CO2's low viscosity, which is 400 times less than that of ICM, it allows for quicker opacification of small vessels compared to iodine, providing crucial details about the beginning and end of stenoses and occlusions in the vessel needing treatment.
.jpg)